
USB4 Cable Specifications: The Future of High-Speed Connectivity
Introduction As technology continues to evolve, the demand for faster, more efficient connectivity solutions has become critical for businesses and
In today’s digital age, USB connectors and cables are ubiquitous. They play a crucial role in connecting devices, transferring data, and powering our gadgets. Understanding the different types of USB connectors and cables is essential for anyone who wants to optimize their technology usage. This comprehensive guide will cover everything you need to know about USB connectors and cables, surpassing any existing guides in depth and detail.
Universal Serial Bus (USB) technology has revolutionized how we connect and interact with our devices. Introduced in the mid-1990s, USB was designed to standardize the connection of peripherals to computers, replacing a variety of earlier interfaces. USB connectors and cables are now used in a wide range of applications, from charging smartphones to connecting keyboards and external hard drives.
Key Features of USB Technology:
| USB Version | Release Year | Key Features | Data Transfer Speed | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USB 1.0 | 1996 | Standardized peripheral connectivity | 1.5 Mbps (Low Speed), 12 Mbps (Full Speed) | Keyboards, mice, printers |
| USB 1.1 | 1998 | Improved performance and reliability | 12 Mbps (Full Speed) | Keyboards, mice, printers |
| USB 2.0 | 2000 | Significant improvement in data transfer and power delivery | 480 Mbps (High Speed) | Flash drives, cameras, external hard drives |
| USB 3.0 | 2008 | Known as SuperSpeed USB, backward compatible with USB 2.0 | Up to 5 Gbps | High-speed storage devices, high-resolution webcams |
| USB 3.1 | 2013 | Known as SuperSpeed+ USB, improved power delivery and efficiency | Up to 10 Gbps | Reversible USB Type-C connectors |
| USB 3.2 | 2017 | Introduced multi-lane operation, consolidated USB 3.x standards | Up to 20 Gbps | Data-intensive applications |
| USB4 | 2019 | Integrates Thunderbolt 3 capabilities, high performance and versatility | Up to 40 Gbps | Multiple data and display protocols |
Description:
USB Type-A is the original USB connector design and remains the most common type. It is typically found on computers, laptops, TVs, and game consoles.
Key Features:
Common Uses:
Insert image of USB Type-A connector.
Description:
USB Type-B connectors are typically used for larger devices, such as printers and external hard drives. The connector is square with a slight bevel on the corners.
Key Features:
Common Uses:
Insert image of USB Type-B connector.
Description:
USB Type-C is the latest USB connector standard, known for its slim, reversible design. It supports higher power and data transfer rates.
Key Features:
Common Uses:
Insert image of USB Type-C connector.
Description:
Micro USB connectors are smaller than Type-A and Type-B, commonly used in mobile devices. There are two versions: Micro-A and Micro-B.
Key Features:
Common Uses:
Insert image of Micro USB connector.
Description:
Mini USB connectors were commonly used before Micro USB became prevalent. They are slightly larger and were used in older mobile devices and cameras.
Key Features:
Common Uses:
Insert image of Mini USB connector.
Description:
USB 3.0 and 3.1 connectors are backward compatible with USB 2.0 but offer significantly higher data transfer rates and power delivery capabilities.
Key Features:
Common Uses:
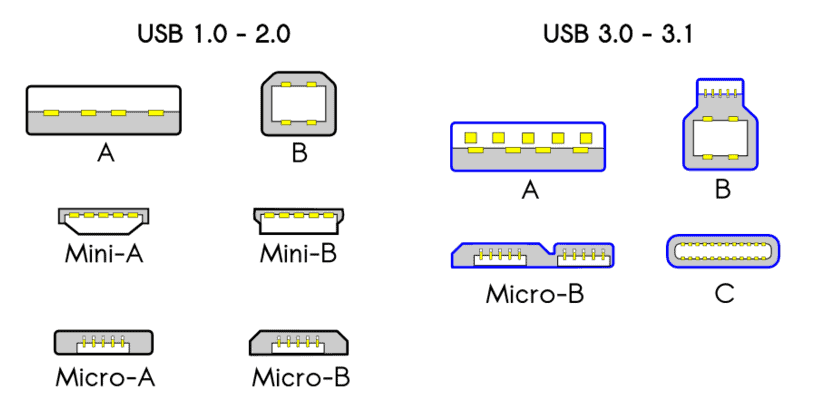
Description:
Standard USB cables are used for general connectivity and charging purposes. They typically feature a USB Type-A connector on one end and various other connectors on the other end, depending on the device.
Common Configurations:
Uses:
Insert a table comparing different standard USB cable configurations and their uses.
Description:
USB On-The-Go (OTG) cables allow devices to act as hosts, enabling direct connection between devices without a computer.
Key Features:
Uses:
Insert an image demonstrating the use of a USB OTG cable with a smartphone.
Description:
USB charging cables are specifically designed for powering and charging devices. They come in various lengths and support different power delivery capabilities.
Key Features:
Uses:
Insert an image of a USB charging cable connected to a smartphone and a power source.
Description:
USB extension cables are used to extend the length of an existing USB connection. They feature a USB Type-A connector on one end and a USB Type-A receptacle on the other.
Key Features:
Uses:
Description:
USB 1.0 was the first version, offering basic connectivity and data transfer capabilities. USB 1.1 improved upon it with better performance and reliability.
Data Transfer Speeds:
Uses:
Insert a chart comparing data transfer speeds of different USB versions.
Description:
USB 2.0, also known as High-Speed USB, brought significant improvements in data transfer rates and power delivery.
Data Transfer Speeds:
Uses:
Description:
USB 3.0, branded as SuperSpeed USB, and USB 3.1, branded as SuperSpeed+ USB, introduced even higher data transfer rates and better power efficiency.
Data Transfer Speeds:
Uses:
Description:
USB 3.2 consolidated previous versions, introducing multi-lane operation to double data transfer rates.
Data Transfer Speeds:
Uses:
Description:
USB4 is the latest version, merging with Thunderbolt 3 technology to provide even higher performance and versatility.
**Data Transfer
Data Transfer Speeds:
Description:
USB4 is the latest version, merging with Thunderbolt 3 technology to provide even higher performance and versatility.
Data Transfer Speeds:
Uses:


When selecting a USB connector and cable, it’s essential to consider several factors to ensure compatibility and optimal performance for your devices.
Description:
Ensure that the USB connector type matches the port on your device. Different devices require different types of connectors, such as USB Type-A, Type-B, Type-C, Micro USB, or Mini USB.
Key Considerations:
Insert a table comparing different devices and their corresponding USB connector types.

Description:
Consider the data transfer speed required for your application. Higher data transfer rates are necessary for tasks like transferring large files, streaming video, or using high-speed peripherals.
Key Considerations:
Insert an infographic showing data transfer requirements for different applications.

Insert an infographic showing data transfer requirements for different applications.
Description:
Ensure the USB cable can provide adequate power for your devices. This is especially important for charging devices and powering peripherals that require more energy.
Key Considerations:
Insert a chart comparing power delivery capabilities of different USB versions.

| USB Version | Power Delivery | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| USB 1.0 | Up to 2.5W (5V, 0.5A) | Basic peripherals (e.g., keyboards, mice) |
| USB 2.0 | Up to 2.5W (5V, 0.5A) | Standard peripherals, small devices |
| USB 3.0 | Up to 4.5W (5V, 0.9A) | High-speed peripherals, external hard drives |
| USB 3.1 | Up to 15W (5V, 3A) | Fast charging for smartphones and tablets |
| USB 3.2 | Up to 100W (20V, 5A) | Charging laptops, high-power devices |
| USB4 | Up to 100W (20V, 5A) | High-performance computing, all-in-one cables |
USB connectors and cables are used in various applications across different industries, from consumer electronics to medical devices.
Description:
USB technology is widely used in consumer electronics for charging, data transfer, and connecting peripherals.
Common Devices:

Insert an image showing various consumer electronics connected via USB.
Description:
In industrial settings, USB technology is used for data acquisition, device control, and communication between machines.
Common Uses:

Insert an image showing USB use in industrial settings.
Description:
USB connectors are increasingly used in vehicles for charging devices, infotainment systems, and connecting diagnostic tools.
Common Uses:

Insert an image showing USB ports in a car.
Description:
In the medical field, USB technology is used for connecting diagnostic equipment, transferring patient data, and powering medical devices.
Common Uses:

Despite their widespread use and reliability, USB connectors and cables can sometimes encounter issues. Here are some common problems and their solutions.
Description:
Issues with connecting devices can be due to damaged connectors, loose connections, or incompatible ports.
Solutions:

Description:
Slow data transfer speeds or failed transfers can result from using outdated cables, insufficient power, or incompatible USB versions.
Solutions:

Description:
Charging issues can occur if the cable or connector is damaged, the power source is insufficient, or the device requires more power than the cable can provide.
Solutions:

USB technology continues to evolve, with new developments aimed at increasing speed, power delivery, and versatility. Here are some trends to watch.
Description:
Future USB versions will likely focus on even higher data transfer speeds to support emerging technologies like 8K video, VR, and AR applications.
Expected Developments:

Description:
As devices become more power-hungry, USB technology will continue to improve power delivery capabilities, supporting faster charging and powering larger devices.
Expected Developments:

Description:
Future USB standards will likely support a broader range of functionalities, including data transfer, power delivery, and video output, all through a single connector.
Expected Developments:

Understanding the different types of USB connectors and cables is essential for optimizing your technology usage. This comprehensive guide has covered everything from the basics of USB technology to the latest trends, helping you make informed decisions about the connectors and cables you need.
Whether you’re connecting peripherals to your computer, charging your smartphone, or transferring data, choosing the right USB connector and cable can significantly enhance your experience. For more information and to explore our range of USB products, visit our product pages.

Introduction As technology continues to evolve, the demand for faster, more efficient connectivity solutions has become critical for businesses and

Understanding the Evolution of USB Connectors In today’s technology-driven world, USB (Universal Serial Bus) connectors are an integral part of

At EDOM Electronics, we take pride in our meticulous approach to manufacturing high-quality USB C to C cables. Today, we’re
WhatsApp us
